Energy and Insulation Notes
Last updated October 11, 2024
By Emma Howland
Temperature differential at the roof is usually greater than above and below grade walls the roof requires more thermal insulation.
R= Thermal Resistance of a given material.
U= 1/Rt Thermal transmittance of a building component or assembly. It is expressed as the rate of heat transfer through a unit area of a building component or assembly
Q= UxAx(ti-to)
Q= Rate of heat flow through a construction assembly, U= Overall coefficient of assembly, A= exposed area of assembly, (ti-to)= difference between inside and outside air temperatures
Batt Insulation: flexible, fibrous thermal insulation of fiberglass or mineral wool made in various thicknesses in 16″ and 24″ widths. Sometimes faced with a vapor retarder of kraft paper
Rigid Foam Insulation: 1-4″ thickness, comes in 2′ wide panels. Expanded polystyrene is used above grade, extruded polystyrene below grade. Cellular glass insulation is fire resistant, impervious to moisture and dimensionally stable but has a lower thermal-resistance value than foamed plastic insulations. Foam plastic insulation is flammable and must be protected by a thermal barrier when used on the interior surfaces of a building.
Spray Foam Insulation: typ. polyurethane that is sprayed or injected into a cavity where it adheres to the surface.
Loose Fill: Consists of mineral wool fibers, granular vermiculite or perlite, or treated cellulosic fibers, poured by hand or blown through a nozzle into a cavity or over a membrande
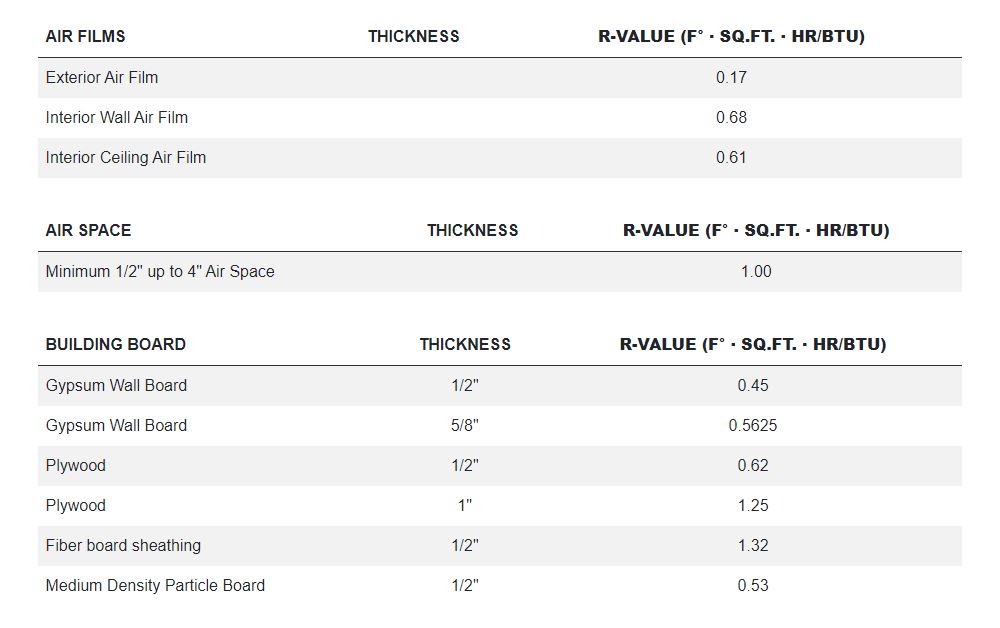
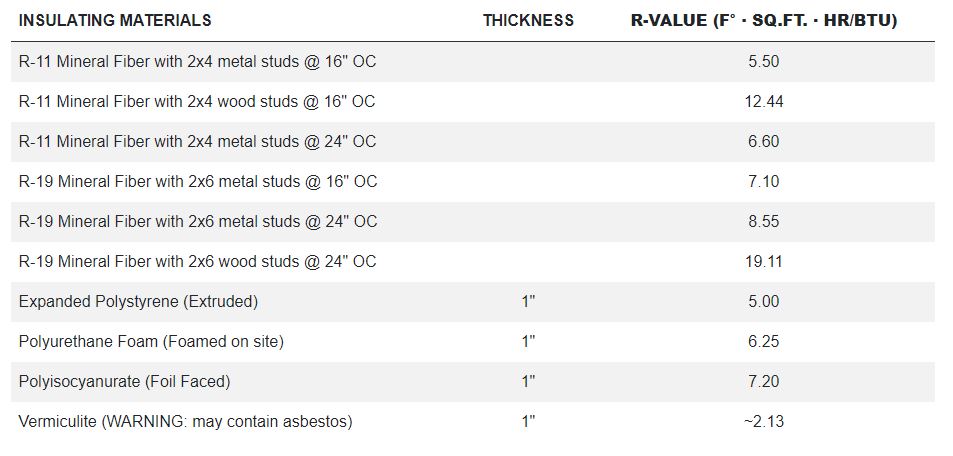
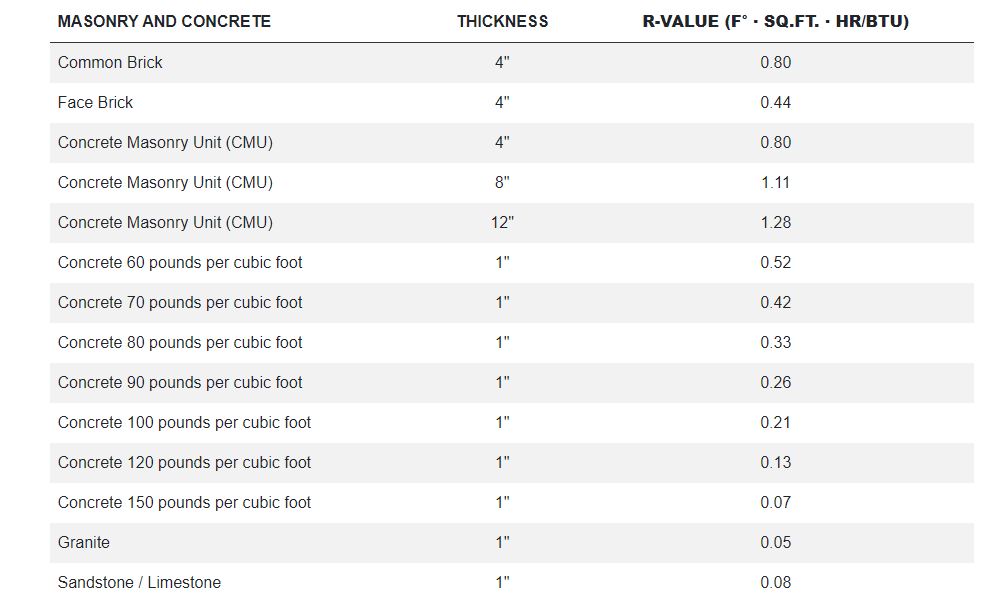
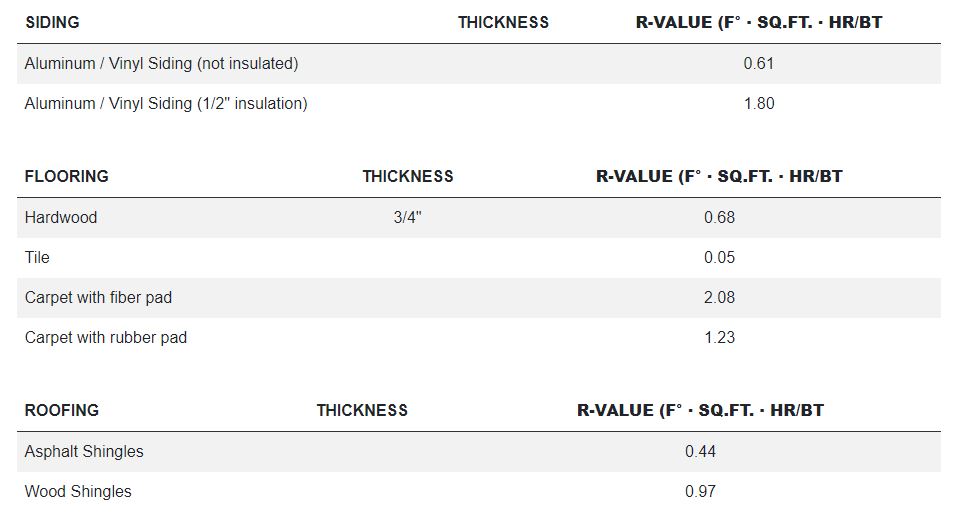
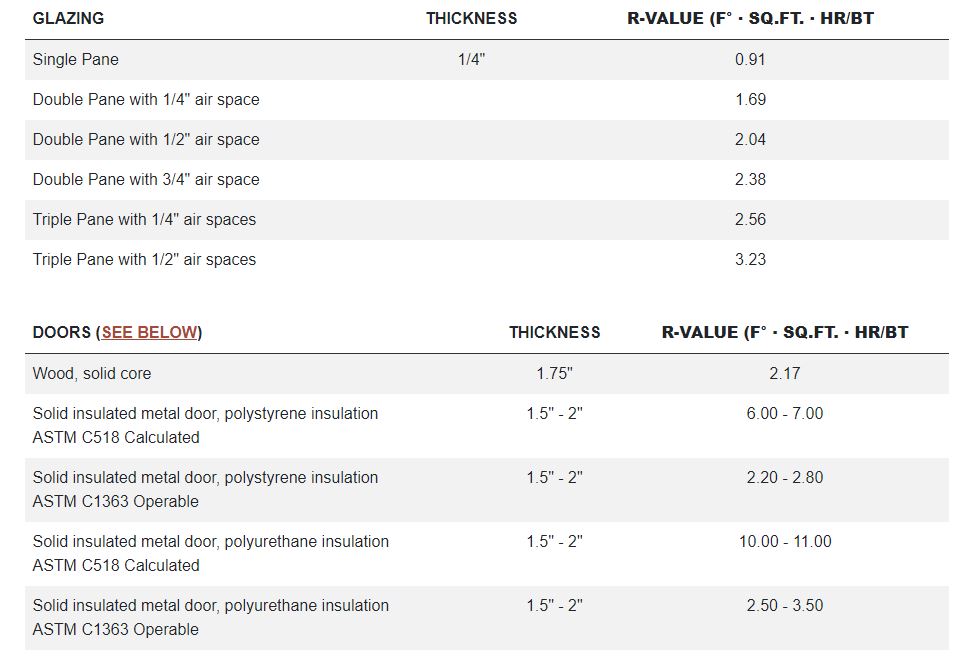
Flat/vaulted ceilings: R38 Blown attic ADV baffled (code baseline) typ. can be used when insulation can be a continuous thickness across the whole roof (like a flat roof). Sloped trusses often need R49 because of short eaves.
Recent Posts
Categories
- Accessibility (2)
- Annotation Templates (1)
- Building Code (6)
- Calculation Templates (2)
- Civil Engineering (3)
- Derivations (8)
- Drafting Standards (18)
- Energy Code (1)
- Geotechnical Engineering (2)
- IT & Software Setup (5)
- Land Use Code (1)
- Product Knowledge (9)
- Production Tutorial (7)
- Research Notes (9)
- Research Tips (1)
- Revit Families (2)
- Revit Tips (5)
- Standard Operating Procedures (6)
- Stormwater (4)
- Structural Calculators (4)
- Structural Engineering (30)
- Structural General (11)
- Uncategorized (29)